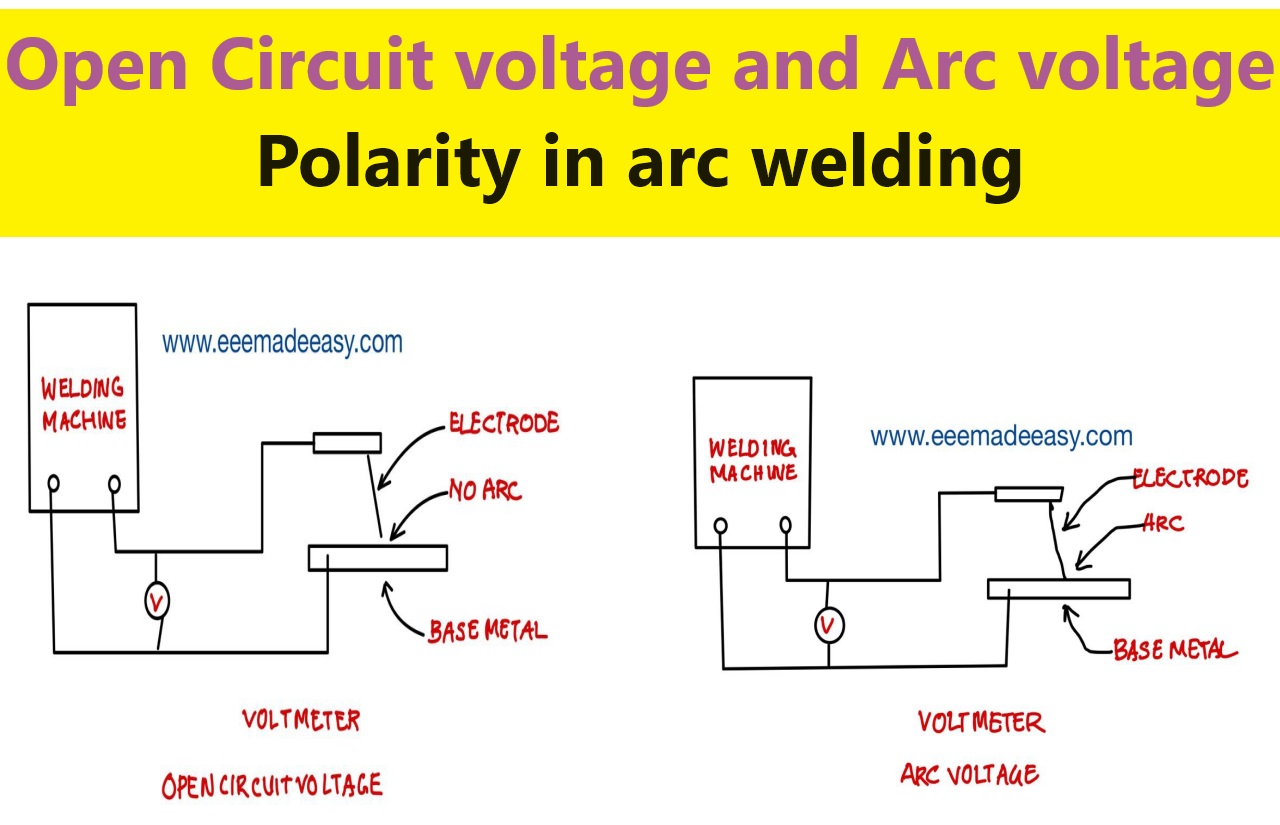
Open Circuit voltage Vs Arc voltage : In this post we will discuss on the difference between open Circuit voltage and Arc voltage.
Figure given below shows an electric circuit used in arc welding.
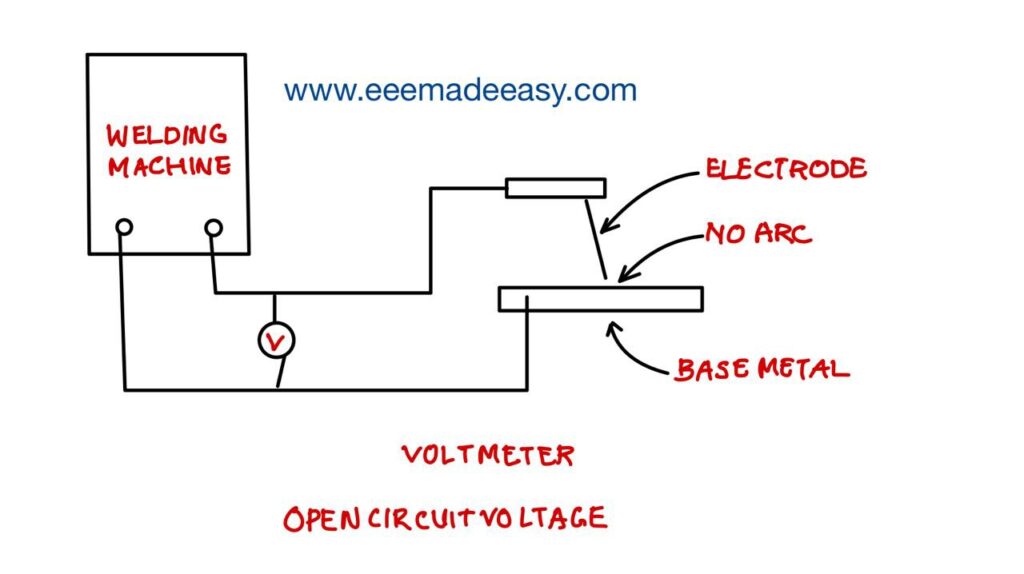
After switching on the welding machine, when there is no arc created/ struck between the electrode tip and the base metal then the voltage “V” shown by the voltmeter in the circuit is called “Open circuit voltage”.
The value of this open circuit voltage will vary from 60V to 110V depending on the type of machine.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
After switching on the welding machine, if the arc is struck/ created between the tip of the electrode and the base metal then the voltage “V” shown by the voltmeter in the circuit is called “Arc voltage”.
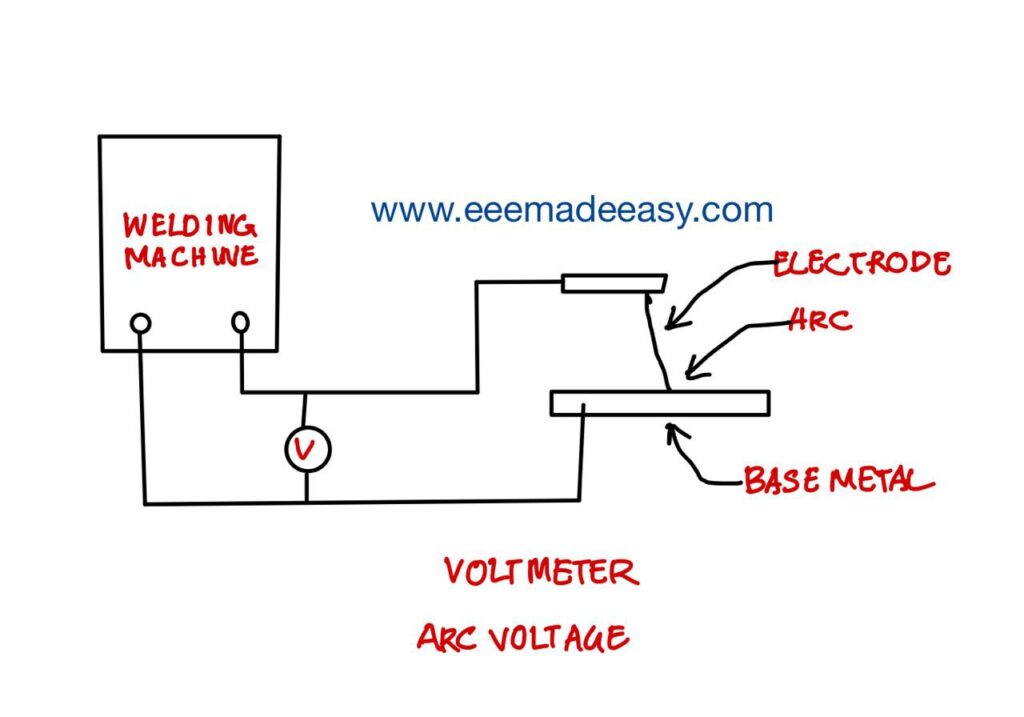
The value of this arc voltage will vary from 18V to 55V depending on the type of machine.
polarity in welding
Importance of polarity in welding
In DC welding 2/3 of the heat liberated from the positive end and 1/3 from the negative
end.
To have this advantage of unequal heat distribution in the electrode and base metal,
the polarity is an important factor for successful welding.
In AC, the polarity can not be utilized as the power source changes its poles
frequently.
Kinds of polarity are two:
- Straight polarity or electrode negative (DCEN).
- Reverse polarity or electrode positive (DCEP).
(i) Straight polarity (DCEN)
In straight polarity the electrode is connected to the negative and the work to the
positive terminal of the power source.
Straight polarity is used for:
welding with bare light coated and medium coated electrodes
welding the thicker sections in down hand position to obtain more base metal fusion and penetration.
(ii) Reverse polarity (DCEP)
In reverse polarity the electrode is connected to the positive and the work to the negative terminal of the power source.
Reverse polarity is used for:
- welding of non-ferrous metals
- welding of cast iron
- welding with heavy and superheavy coated electrodes
- welding in horizontal, vertical and overhead positions
- sheet metal welding.
DC is preferred to AC for hard facing and stainless steel welding.
Choice of the polarity also depends on the instruction of the electrode manufacturers.
In order to get the best results, it is essential to attach the electrode with the correct terminal of the welding machine.
Indication of wrong polarity
If the electrode is used on wrong polarity it will result in:
- excess spatter and poor penetration
- improper fusion of the electrode
- heavy brownish deposition on the face of the weld metal
- difficulty in manipulation of the arc
- abnormal sound of the arc
- poor weld bead appearance with surface defects and more spatter.
Read more on Electric Welding
- [Set 2]MCQ’s on Electrical Welding|Electrical Welding MCQ Questions and Answers|KSEB Sub Engineer
- [Set 1]MCQ’s on Electrical Welding|Electrical Welding MCQ Questions and Answers|KSEB Sub Engineer
- Electric Welding|Resistance welding Electric Arc Welding
- Resistance Welding|Types of Resistance Welding
- Electric arc welding|Types of Electric Arc welding
- Electric Arc length|Short,Medium, Long Arc
- Open Circuit voltage and Arc voltage|Polarity in arc welding
- Arc Welding Equipments|Arc Welding tools and Accessories
- Arc welding safety|shielded metal arc welding preparation & safety
- Methods of joining metals|Metal Joining Methods
- Types of welds|Weld types
- Applications of Welding|Welding Applications
Books on Welding
Join EEE Made Easy Telegram channel
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus