Cells and Batteries- Here types of cells, Charging and discharging of batteries, Forming, buckling, sedimention are explained. Daniel, Ediso, Leclanche cell etc are explained
What is a cell?
A cell is a device meant for generating e.m.f.on account of chemical
reactions.
- Grouping of Cells|Series, parallel and Mixed Cell combinations
- MCQ’s on Cells and Batteries|Cells and batteries Objective Questions
- Cells and batteries
- Basic Electrical Engineering Quiz | Cells and Batteries Quiz
- Cells and batteries
- Primary and secondary cells|Cells and Batteries
- Battery Capacity Tester|Battery Tester
What is a battery?
A battery is a group of cells.
What is meant by primary and secondary cells ?
The cell in which an e.m.f. is generated on account of chemical actions is called a primary cell and the cell in which electrical energy
is stored in the form of chemical changes is called a secondary cell.
Who made the first primary cell ?
Famous scientist Mr. Volta made the first primary cell which is called
a ‘Voltaic cell’.

What are the constituents of a voltaic cell ?
A Voltaic cell consists of a voltmeter (container), dilute sulphuric acid as an electrolyte, copper rod as an anode and zinc rod as a cathode.
What is electrolysis ?
The process of changing the composition of a chemical solution by passing an electric current through the same is known as electrolysis.
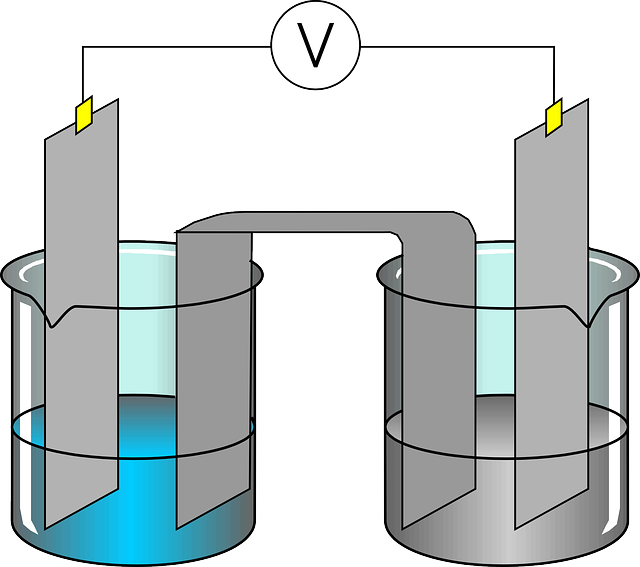
What is meant by an electrolyte ?
The chemical solution which undergoes chemical changes on ac
count of conduction of electric current is called electrolyte.
What do you mean by anode and cathode ?
in a cell, in electrode (metallic rod) through which the current
enters an electrolyte is called cathode and the electrode through which the current leaves the electrolyte is called an anode.
What is an ion ?
A charged atom is called an ion.
What is ionisation ?
The process in which atoms are changed into ions is called ionisation.
What is a cation and an anion ?
A positive ion is called a cation and a negative ion is called an anion.
What are the Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis ?
The mass of the element liberated at an electrode is proportional to the amount of current passed through the electrolyte. m=ZIt [where, Z electro chemical equivalent)
(i) When equal amounts of current are passed through different electrolytes, the masses of elements liberated at the respective electrodes are proportional to their chemical equivalents
m1/W1 = m2/W2
What is electro chemical equivalent ?
The mass of an element liberated/dissolved by one coulomb of charge is called E.C.E.
What is chemical equivalent ?
The number of parts by weight of an element which combines with or displaces 1.008 parts by weight of hydrogen is called chemical
equivalent.
What are the applications of electrolysis ?
Electrolysis is used in electroplating, purification of metals, extract tion of metals, electroplating etc.
What chemical reactions take place in a Voltaic cell ?
Dilute sulphuric acid decomposes into hydrogen and sulphate ions.
H2SO4 = 2H+ + SO4 2-, H,
Sulphate ions reach at zinc rod and make it negative : Zn2+ + SO4 2- = ZnSO,
Hydrogen ions reach at copper rod and make it positive :
2H+ + 2e = H2,
What are the defects of a Voltaic cell ?
The main defects of a voltaic cell are local action and polarisation.
What do you mean by local action ?
The loss of electrical energy due to formation of a number of tiny
cells within the impure zinc rod is called local action.
How local action is eliminated ?
It is minimised by amalgamating the zinc rod (coating the zinc rod
with mercury). The mercury covering doesn’t allow the zinc impurities to take part into chemical actions.
What is meant by polarisation ?
The hydrogen ions liberated at the carbon anode make it non
conducting after some time, the phenomenon is referred as polaris
tion.
How polarisation is eliminated ?
Polarisation is minimised by employing the granules of manganese dioxide (Mno,) around the carbon anode which converts hydrogen ions into water:
Mno2 +2H =Mn2O3, + H2O
What is a Leclanche cell?
It is an improved type of voltaic cell in which ammonium chloride (NH CI) is filled in a zinc container which acts cathode. The carbon anode is placed in a porous pot filled with MnO, granules.
What is a dry cell ?
A dry cell is a compact form of Leclanche cell. It employs a paste consisting of ammonium chloride, zinc chloride and plaster of paris.
What is a Daniel cell ?
Mr Daniel employed a copper sulphate solution as a depolariser in
place of MnO, and rest of the construction of his cell was similar to
that of Voltaic cell.
What is meant by the internal resistance of a cell ?
The resistance offered by a cell to the flow of electric current through itself is called the internal resistance of the cell.
What is the difference between e.m.f.and the terminal voltage of a cell/battery ?
The open circuit voltage of a cell/battery is known as e.m.f. while the voltage available across the cell/battery in a closed circuit is known
as terminal voltage or p.d.
Why cells are joined in series ?
Cells are joined in series in order to obtain a large e.m.f. E,=n.E. .
Why cells are joined in parallel ?
Cells are joined in parallel in order to obtain a high amount of current.
I= nE/(R+nr)
I = circuit current, amps.
n = no. of cells
E = e.m.f. of one cell, volts
R = load resistance, ohms
r = internal resistance of one cell,ohms.
where,
What is a lead-acid cell ?
A lead-acid cell is a secondary cell and it is commonly referred as an accumulator. It consists of positive plate (lead peroxide), negative plates (spongy lead), dilute sulphuric acid ‘ a hard rubber con tainer.
What is forming ?
Originally, the positive and negative plates of a lead-acid cell are made of red lead (Pb3O4) and litharge (PbO) respectively. On filling the cell with dilute H2SO4, chemical actions are started and the positive plates get turned into PbO2, while negative plates get turned into Pb. This process is known as forming.
What chemical reactions take place during charging of a lead-acid cell ?
H2SO4 = 2H+ + SO4 2-
At cathode : PbSO4 + 2H+ = Pb + H2SO4,
At anode: PBSO4 + SO4 2- + 2H2O = PbO2 + 2H2SO4
What chemical reactions take place during discharging of a lead- acid cell ?
H2SO4 = 2H+ + SO4 2-
At cathode : Pb + SO4 2- = PbSO4
At anode : PbO2 + 2H+ + H2SO4 = PbSO4 + 2H2O
How will you identify that a lead-acid cell has stored charged ?
The S.G.of the electrolyte of charged lead-acid cell rises upto 1.25
1.28 and the e.m.f. becomes 2.1 to 2.2 volts per cell.
How will you identify that a lead-acid cell has discharged ?
The S.G. of the electrolyte of a discharged lead-acid cell drops to
1.15-1.18 and the e.m.f. drops to 1.8 volts.
How S.G. is measured ?
S.G. is measured by a hydrometer.
What is S.G.?
S.G. means specific gravity or specific density. The ratio of the density of a liquid to the density of 4°C water is referred as S.G.
What is hydrometer ?
Hydrometer is an instrument meant for the measurement of S.G. of
a solution. It is based on the principle of Archimedes.
What is meant by AHC ?
AHC means ampere hour capacity of a cell. It is equal to the product of amperes and the hours for which the cell/battery is capable to work.
What is the purpose of a ‘high rate discharge tester’?
It is meant for testing the charge condition or the terminal voltage of a lead-acid cell.
How will you identify the (+) and (-) terminals of a battery?
Terminals are identified with the help of a DC voltmeter.
What are the main steps to be taken for the maintenance of batteries ?
(i) Battery terminals should be cleaned with a cloth soaked in warm water and then dried periodically, then apply a small quantity of grease on the terminals.
(ii) Keep the battery tight to the vehicle’s body and keep the vent plug tight iii) Keep the battery plates will immersed in the electrolyte. Add distilled water as and when required.
iv) Don’t leave the battery idle.
What are the precautions to be observed during battery charging?
(i) Charge the battery in an airy room. current rate should not be more
(ii) Charging (iii) Remove the vent plugs during charging than 3 to 6 amperes.
(iv) Keep flames etc. away from the battery.

What is constant current charging method ?
In this method the charging current rate is maintained at a constant
value by changing the number of bulbs (loads).
What is constant voltage charging method ?
In this method, charging voltage is maintained at a constant value. Hence, the rate of initial charging current rests higher than the final charging current.
What is a battery charger ?
Battery charger is an instrument used for battery charging purposes with AC supply.
What are the merits of a lead-acid battery ?
(i) More terminal voltage
(ii) Rechargable
(iii) It supplies a steady current.
What is sulphation ?
The deposition of a hard layer of lead sulphate on the plates of a lead-
acid cell is called sulfation. A battery should not be left idle so that the battery plates do not get sulphated.
What is trickle charging ?
A Sulphated battery can be revived by charging it at a very low current rate for a long time. The process is called trickle charging.
What is sedimentation ?
The formation of a pile of sediment at the bottom of a lead-acid cell is known sedimentation. In order to eliminate this defect always use
distilled water.
What is buckling ?
The bending of cell plate is called buckling. Do not charge or discharge a battery at a high current rate in order to avoid buckling.
What is corrosion ?
The formation of an insulating layer on the battery terminals is called corrosion. It is a routine defect and it can be reduced by periodically cleaning and greasing the battery terminals.
How can you preserve a battery for a long time in an unused state?
Remove battery electrolyte, wash and dry the battery inner portion and then store it.
What is an alkaline cell ?
It consists of an alkali electrolyte.
What is Edison cell ?
Edison cell (or nickel-iron cell) consists of nickel plated steel tubes which are perforated and are filled with a paste of nickel-hydroxide [N/OH),]to act as positive plates. The pockets of negative plates are filled with ferrous hydroxide [Fe(OH),]. Caustic-potash and lithium hydroxide (LiOH) mixture is used as an electrolyte.
What are the chemical reactions which take place in an Edison cell?
During charging :
At anode :
At cathode:
KOH – K+ + OH-
Ni(OH)2 + 2OH – → Ni(OH)4
Fe (OH)2 + 2K+ → Fe + 2KOH
During discharging:
At anode :
Ni(OH)4 + 2K = Ni(OH)2 + 2KOH
At cathode :
Fe + 2OH =Fe(OH)2
What is the e.m.f. of an Edison cell ?
Its e.m.f. is 1.4 V in charged state and 1.1 V in discharged state.
What is nickel-cadmium cell ?
A nickel-cadmium or Junger cell is an alkaline cell in which active materials are nickel-hydroxide and cadmium
What are the merits of Alkaline cell w.r.t. lead-acid cell ?
(1) Alkaline cell can withstand heavy current rate discharging.
(ii) It is light in weight and it is mechanically rigid.
(ii) It has no sulphation defect.
(iv) It is most suitable for electric operated vehicles.
What is meant by the efficiency of a secondary cell ?
(AH delivered by the cell /AH supplied to the cell )X 100
What is electroplating?
Electroplating is an application of electrolysis. In this process a thin film of a nobler metal is deposited on the baser metal by means of electrolysis.
nickel is released from ____ ?
. Cells and Batteries Questions
Basic Electrical Questions and Answers
Primary cells and Secondary cells
Sub Engineer Previous Questions
Basic Electrical MCQ EEE Notebook
Polylecturer Electronics Notes
Previous Question Papers Download
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus
- Basic Electrical Engineering Quiz | Cells and Batteries Quiz
- [PDF]RRB Technician Syllabus 2024| Exam Pattern RRB Technician
- Measurement of High Resistance
- HVDC vs HVAC |Comparison of HVAC and HVDC
- Electrical Distribution System
| Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ’s From Notebook Site (www.notebukofaprofessor.blogspot.com) |
| 1. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 1 |
| 2. Current Electricity MCQ |
| 3. Basic Electrical MCQ 2 |
| 4. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 3 |
| 5. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 4 |
| 6. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 5 |
| 7. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 6 |
| 8. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 7 |
| 9. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 8 |
| 10. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 9 |
| 11. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 10 |
| 12. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 11 |
| 13. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 2 |
| 14. Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ 14 |











