PSU – Power Supply Unit
Power supply units provide the necessary power, voltage and current requirements for electronic devices.
Read also about UPS – Uninterrupted Power Supplies
EEE Made Easy store for useful books
Theyusuallychangeactodcvoltage. – For example, 120 volts ac is changed to 12 volts dc.
Basic elements of power supply unit circuits
- Transformer – steps ac voltage up or down.
- Rectifier Diodes – change ac to “ripple” dc.
- Filter Network – includes capacitors and inductors, smooth out the ripples.
- Voltage Regulator – keeps the voltage constant.
cLASSIFICATION OF POWER SUPPLIES
Based on the regulation concept power supplies are classified as under,
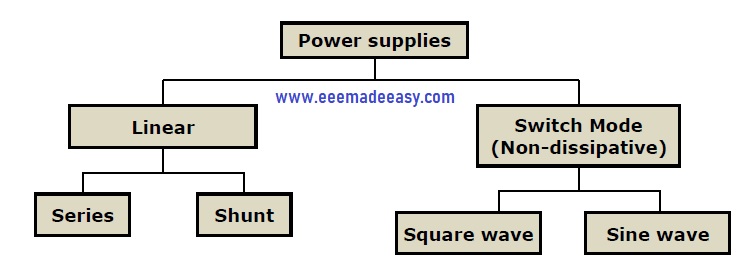
Linear Power supplies (LPS)
Linear Power supplies include a Mains transformer, rectifier, filter and regulator (series or shunt type).
In this the active device that provides regulation is always operated in the active or linear region of its characteristics.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Any change in the output voltage due to a change in input voltage or load current results in a change in the drop across the regulator transistor( in case of series regulator) or a change in the current through the regulator transistor ( in case of shunt regulator) so as to maintain a constant output voltage across the load.
Switch Mode Power supplies
In a Switch mode power supply(SMPS), the active device that provides regulation always operates in a Switched mode i.e., It is operated either in cut-off or in saturation
What is SMPS?
Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) is an electrical power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently.
It transfers power from a source to a load, while converting voltage and current characteristics.
Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time.
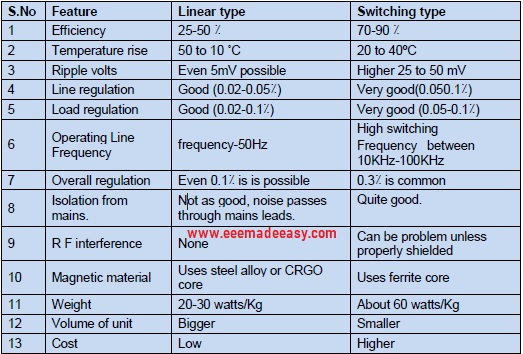
Linear Mode Supply Vs SMPS
Comparison between Linear Mode Supply and SMPS
Types of SMPS
- Fly back mode power supply
- Forward mode power supply
Fly back Mode SMPS Power Supplies
Used where power requirement is less than 100W.
These are simple in design using minimum components and minimum circuit board space.
Reliable in operation and the efficiency is 70% to 80 %.
Forward Mode SMPS Power Supplies
Used for power requirement up to 200 watt.
Efficiency up to 90 %
Not very common due to complicated design. Mostly used for DC to DC conversion systems
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
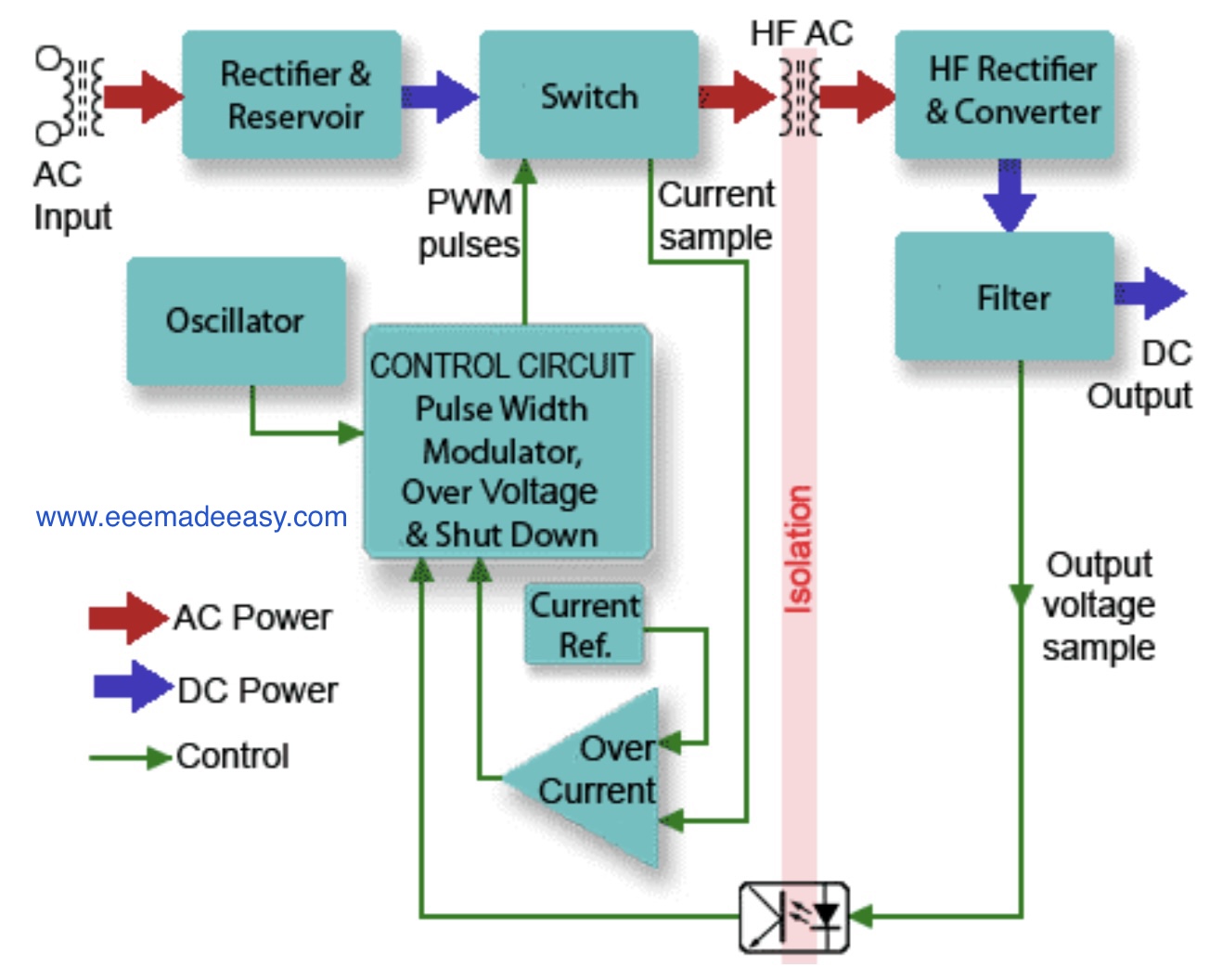
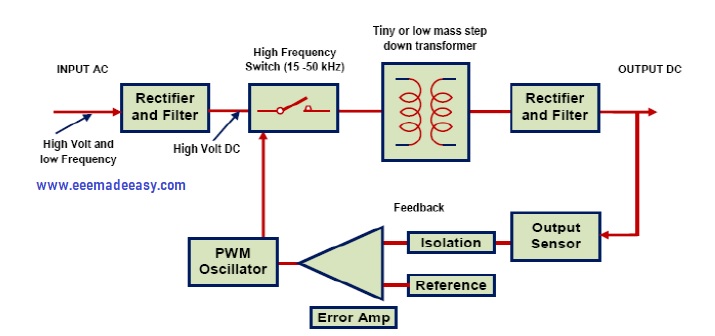
Functional Block Diagram of SMPS
Below is the smps block diagram
Advantages of SMPS
- Lower weight
- Smaller size
- Higher efficiency
- Lower power dissipation
- Wide ac input voltage range
- Reduced costs
Disadvantage of SMPS
- The complexity of the circuit
- tendency to RFI radiation
- slower response to rapid load changes
- less ability to remove output ripple.
Applications of SMPS
- Machinetoolindustries
- SecuritySystems (Closed circuit cameras)
- SupportsupplieswithPLC’s
- personal computers
- MobilePhonechargers
Examples of SMPS
Zebronics 450 W, iball 600W, Antec 750W, Cooler master 550W, Seasonic 500w, UMAX 450W,Corsair 750W, Artis 400W
Working of SMPS
SMPS can be used to convert AC to DC, such as in a desktop computer power supply, or DC to DC, either step up or step down in many different Battery powered systems.
The input is the AC mains (line) supply the AC is rectified and smoothed by a reservoir capacitor before being processed by what is in effect a DC-to-DC converter, to produce a regulated DC output at the required level.
Fig. shows a block diagram example of a typical SMPS with an AC Mains (line) input and a regulated DC output.
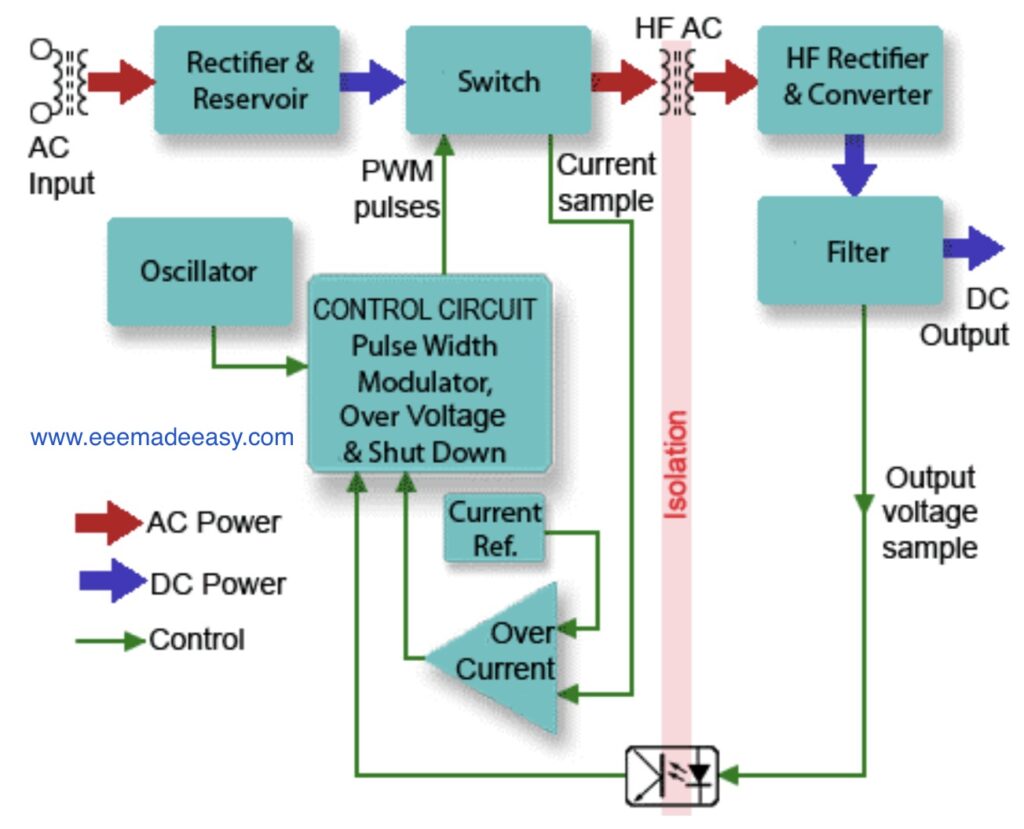
The output rectification and filter are isolated from the High-Frequency switching section by a high-frequency transformer, and voltage control feedback is via an optoisolator.
The control section is typical of specialist ICs containing an HF oscillator, pulse width modulation, voltage, and current control and output shutdown sections.
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus
- Basic Electrical Engineering Quiz | Cells and Batteries Quiz
- [PDF]RRB Technician Syllabus 2024| Exam Pattern RRB Technician
- Measurement of High Resistance
- HVDC vs HVAC |Comparison of HVAC and HVDC
- Electrical Distribution System