IE Rules:The Indian Electricity Rules 1956 was made under section 37 of the Indian Electricity Act, 1910 and redefined after enactment of The Electricity Act 2003
Indian Electricity (IE) Rules 1956
Indian Electricity Rules were first made by the Central Electricity Board in the exercise of powers conferred under the Indian Electricity Act, of 1910.
Read: [PDF] Electricity Act 2003|Indian Electricity Act 2003 PDF
CEAR – Central Electricity Authority (Measures relating to Safety and Electric Supply) Regulations, 2010 came into effect from 20th September 2010, in place of The Indian Electricity Rules, 1956.
Read : Which IE rule is applicable to service mains?|Indian Electricity Rule
Importance of IE Rules
IE rules mainly dealt with the following;
- Appointment of inspectors & their duties
- Licensing provisions.
- General safety requirements
- Conditions relating to supply and use of energy.
- Electric supply lines and systems for LV & MV
- Electric supply lines and systems for HV & EHV.
- Overhead lines, underground cables and generating stations
- Electric traction.
- Precautions in mines & oil fields
Electricity Rules in India have been retained in the Electricity Act, 2003 and will continue to be in force until the regulations/rules under Section 53 of the Electricity Act, 2003 are framed.
There are 143 IE rules in all and we will discuss the relevant ones in brief. lets first check the definitions of different gradations of voltages as given by these rules.
Check : Indian Electricity Rules 1956
Read also: [Updated]List of IS Codes Electrical standards|IS 732, IS 3043 etc|Indian electrical standards
Indian Electricity Rules List
Chapter 1 – Preliminary
IE Rule 1 Short title and commencement
IE Rule 2 Definitions
IE Rule 3 Authorisation
Chapter II -Inspectors
IE Rule 4 Qualification of Inspectors
IE Rule 4A Appointment of officers to assist the Inspectors
IE Rule 4B Qualification of officers appointed to assist the Inspectors
IE Rule 5 Entry and inspection
IE Rule 6 Appeals
IE Rule 7 Amount of fees
IE Rule 8 Incidence of fees recoverable in the cases of dispute
IE Rule 9 Submission of records
IE Rule 10 List of consumers
Chapter III – Licence
IE Rule 11 Application for licence
IE Rule 12 Copies of maps and draft licence for public inspection
IE Rule 13 Contents of draft licence
IE Rule 14 Form of draft licence
IE Rule 15 Advertisement of application and contents thereof
IE Rule 16 Amendment of draft licence
IE Rule 17 Local enquiries
IE Rule 18 Approval of draft licence
IE Rule 19 Notification of grant of licence
IE Rule 20 Date of commencement of licence
IE Rule 21 Deposit of maps
IE Rule 22 Deposit of printed copies
IE Rule 23 Application for written consent of State Government in certain cases
IE Rule 24 Amendment of licence
IE Rule 25 Sale of Plans
IE Rule 26 Preparation and submission of accounts
IE Rule 27 Model conditions of supply
IE Rule 28 Forms of requisitions
Chapter IV – General Safety Requirements
IE Rule 29 Construction, installation, protection, operation and maintenance of electric supply lines and apparatus
IE Rule 30 Service lines and apparatus on consumer’s premises
IE Rule 31 Cut-out on consumer’s premises
IE Rule 32 Identification of earthed and earthed neutral conductors and position of switches and cut-outs therein.
IE Rule 33 Earthed terminal on consumer’s premises
IE Rule 34 Accessibility of bare conductors
IE Rule 35 Danger notices
IE Rule 36 Handling of electric supply lines and apparatus
IE Rule 37 Supply to vehicles, cranes, etc.
IE Rule 38 Cables for portable or transportable apparatus
IE Rule 39 Cables protected by bituminous materials
IE Rule 40 Street boxes
IE Rule 41 Distinction on different circuits
IE Rule 41A Distinction of the installations having more than one feed
IE Rule 42 Accidental charge
IE Rule 43 Provisions applicable to protective equipment
IE Rule 44 Instructions for restoration of persons suffering from electric shocks
IE Rule 44A Intimation of accident
IE Rule 45 Precautions to be adopted by consumers, owners, occupiers,electrical contractors, electrical workmen and suppliers
Join EEE Made Easy Telegram channel
IE Rule 46 Periodical inspection and testing of consumer’s installation
Chapter V -General Conditions Relating To Supply And Use Of Energy
IE Rule 47 Testing of consumer’s installation
IE Rule 47A Installation and Testing of Generating Units
IE Rule 48 Precautions against leakage before connection
IE Rule 49 Leakage on consumer’s premises
IE Rule 50 Supply and use of energy
IE Rule 50A Additional provisions for supply and use of energy in multistoreyed building (more than 15 metres in height)
IE Rule 51 Provisions applicable to medium, high or extra high voltage installations
IE Rule 52 Appeal to Inspector in regard to defects
IE Rule 53 Cost of inspection and test of consumer’s installation
IE Rule 54 Declared voltage of supply to consumer
IE Rule 55 Declared frequency of supply to consumer
IE Rule 56 Sealing of meters and cut-outs
IE Rule 57 Meters, maximum demand indicators and other apparatus on consumer’s premises
IE Rule 58 Point of commencement of supply
IE Rule 59 Precautions against failure of supply; Notice of failures
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Chapter VI -Electric Supply Lines, Systems And Apparatus For Low And Medium Voltages
IE Rule 60 Test for resistance of insulation
IE Rule 61 Connection with earth
IE Rule 61A Earth leakage protective device
IE Rule 62 Systems at medium voltage
Chapter VII -Electric Supply Lines, Systems And Apparatus For High And Extra-High Voltages
IE Rule 63 Approval by Inspector
IE Rule 64 Use of energy at high and extra-high voltages
IE Rule 64A Additional provisions for use of energy at high and extra-high voltages
IE Rule 65 Testing, operation and maintenance
IE Rule 66 Metal sheathed electric supply lines; Precautions against excess leakage
IE Rule 67 Connection with earth
IE Rule 68 General conditions as to transformation and control of energy
IE Rule 69 Pole type sub-stations
IE Rule 70 Condensers
IE Rule 71 Additional provisions for supply to high voltage luminous tube sign installation
IE Rule 72 Additional provisions for supply to high voltage electrode boilers
IE Rule 73 Supply to X-ray and high frequency installation
Chapter VII -Overhead Lines
IE Rule 74 Material and strength
IE Rule 75 Joints
IE Rule 76 Maximum stresses; Factors of safety
IE Rule 77 Clearance above ground of the lowest conductor
IE Rule 78 Clearance between conductors and trolley wires
IE Rule 79 Clearances from buildings of low and medium voltage lines and service lines
IE Rule 80 Clearances from buildings of high and extra-high voltage lines
IE Rule 81 Conductors at different voltages on same supports
IE Rule 82 Erection of or alteration to buildings, structures, flood banks and elevation of roads
IE Rule 82A Transporting and Storing of material near overhead lines
IE Rule 83 Clearances; General
IE Rule 84 Routes; Proximity to aerodromes
IE Rule 85 Maximum interval between supports
IE Rule 86 Conditions to apply where telecommunication lines and power lines are carried on same supports
IE Rule 87 Lines crossing or approaching each other
IE Rule 88 Guarding
IE Rule 89 Service-lines from overhead lines
IE Rule 90 Earthing
IE Rule 91 Safety and protective devices
IE Rule 92 Protection against lightning
IE Rule 93 Unused overhead lines
Chapter IX -Electric Traction
IE Rule 94 Additional rules for electric traction
IE Rule 95 Voltage of supply to vehicle
IE Rule 96 Insulation of lines
IE Rule 97 Insulation of returns
IE Rule 98 Proximity to metallic pipes, etc.
IE Rule 99 Difference of potential on returns
IE Rule 100 Leakage on conduit system
IE Rule 101 Leakage on system other than conduit system
IE Rule 102 Passengers not to have access to electric circuit
IE Rule 103 Current density in rails
IE Rule 104 Isolation of sections
IE Rule 105 Minimum size and strength of trolley-wire
IE Rule 106 Height of trolley-wire and length of span
IE Rule 107 Earthing of guard wires
IE Rule 107A Proximity to magnetic observatories and laboratories
IE Rule 108 Records
Chapter X – Additional Precautions To Be Adopted In Mines And Oil-Fields
IE Rule 109 Application of Chapter
IE Rule 110 Responsibility for observance
IE Rule 111 Notices
IE Rule 112 Plans
IE Rule 113 Lighting, communications and fire precautions
IE Rule 114 Isolation and fixing of transformer, switch-gear, etc.
IE Rule 115 Method of earthing
IE Rule 116 Protective equipment
IE Rule 117 Earthing metal, etc.
IE Rule 118 Voltage limits
IE Rule 119 Transformers
IE Rule 120 Switchgear and Terminals
IE Rule 121 Disconnection of supply
IE Rule 122 Cables
IE Rule 123 Flexible cables
IE Rule 124 Portable and transportable machines
IE Rule 125 Sundry precautions
IE Rule 126 Precautions where gas exists
IE Rule 127 Shot-firing
IE Rule 128 Signalling
IE Rule 129 Haulage
IE Rule 130 Earthing of neutral points
IE Rule 131 Supervision
IE Rule 132 Exemptions
CHAPTER XI – MISCELLANEOUS
IE Rule 133 Relaxation by Government
IE Rule 134 Relaxation by Inspector
IE Rule 135 Supply and use of energy by non-licensees and others
IE Rule 136 Responsibility of Agents and Managers
IE Rule 137 Mode of entry
IE Rule 138 Penalty for breaking seal
IE Rule 138A Penalty for breach of rule 44A
IE Rule 139 Penalty for breach of rule 45
IE Rule 140 Penalty for breach of rule 82
IE Rule 140A Penalty for breach of rule 77, 79 or 80
IE Rule 141 Penalty for breach of rules
IE Rule 142 Application of rules
IE Rule 143 Repeal
Definition of Different Grades of Voltages
| VOLTAGE | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| Low Voltage | Not exceeding 250 V |
| Medium Voltage | Not exceeding 650 V |
| High Voltage | Not exceeding 33 kV |
| Extra High Voltage | Exceeding 33 kV |
The above table gives the definitions of different gradations of voltages as given by the IE Rules.
IE Rule 1
The first two rules give the title and definitions of the IE Rules.
IE Rule 3
Rule 3 pertains to authorisation of persons engaged in generation, transformation,
transmission, conversion, distribution or use of energy.
IE Rule 32(A)
As per rule 3(2A), no person should be authorized to operate or undertake maintenance of any part or whole of a generating station of capacity 100 MW and above together with the associated substation and other substations of 132 kV and above unless s/he is adequately qualified and has successfully undergone the type of training specified in the Indian Electricity Rules, 1956.
According to these Rules all work on major electrical installations should be carried out under the permit to work system, which provides in-built safety to the workforce engaged in electrical work.
IE Rule 4 -10
The qualifications and powers of Inspectors and his/her assistants are mentioned in the Rules 4 to 10.
IE Rule 11- 28
Rules 11 to 28 spell out the procedure for applying and obtaining licenses.
IE Rule 29-46
Rules 29 to 46 pertain to the general safety requirements and we state, in brief, the important ones:
Indian Electricity Rule – 29
All electrical apparatus and supply lines should be of appropriate ratings.
• All electric supply lines and apparatus should be constructed, installed, worked and maintained in such a manner as to ensure the safety of personnel and property.
• Identification of earthed and earthed neutral conductors and position of switches and cut outs is a must. In the double pole switches, link should be provided instead of fuse carrier on the neutral conductor.
• Earthed terminal must be provided on consumer’s premises. Earth pits should be constructed and maintained strictly as per relevant standards. The earth resistance of earth electrodes should not exceed 5 ohms.
• Danger Boards as per IS 2551 should be affixed permanently in a conspicuous position on every motor, generator, transformer and other electrical equipment.
• Instructions for restoration of persons suffering from electric shock should be written in English or Hindi or local language of the district and be affixed by the owner in a conspicuous place in every generating station, enclosed switched station, etc.
• If any accident involving a human being or an animal occurs, a telegraphic report within 24 hours of the knowledge of the occurrence of the fatal accident and a written report in the form set out within 48 hours of fatal and other accidents should be sent to the electrical inspector.
Where practicable, a telephonic message should be given to the Inspector immediately.
• Periodic inspection and testing of consumer’s installation must be done at intervals not exceeding five years either by an Inspector or any officer appointed to assist the Inspector or by the supplier as directed by the Central Government.
IE Rule 47- 59
Rules 47 to 59 pertain to the general conditions relating to supply and use of energy.
As per these rules, electrical installation works of a consumer should be carried out by a licensed contractor, the insulation resistance should be above the prescribed limit, and the supplier should not permit the voltage, at the point of commencement of supply, to vary from the declared voltage as per the stipulations given ahead:
• in the case of low or medium voltage by more than 6%;
• in the case of high voltage, by more than 6% on the higher side and by more than 9% on the lower side; and
• in the case of extra high voltage, by more than 10% on the higher side and by more than 12.5% on lower side.
Moreover, a supplier should not permit the frequency of an AC supply to vary from the declared frequency by more than 3%.
There are rules pertaining to electric supply lines, systems and apparatus for low and medium voltages, high and extra high voltages, and additional provisions of supply to high voltage luminous tube sign installations, high voltage electrode boilers, X-ray and high frequency installations.
The supply of energy should not be commenced by the supplier unless and until the inspector is satisfied and the written approval of the Inspector has been obtained.
IE Rule 74 -93
Overhead lines are covered under the Rules 74 to 93.
The factor of safety for various supports is as under:
1) Metal supports 1.5
2) Mechanically processed concrete supports 2.0
3) Hand-moulded concrete supports 2.5
4) Wood supports 3.0
minimum clearance above ground of the lowest conductors
The minimum clearance above ground of the lowest conductors along and across a street is given in Table.
| VOLTAGE LINES PLACE | Low and Medium Voltage Lines | High Voltage Lines |
| Across the street | 5.8 m | 6.1 m |
| Along the street | 5.5 m | 5.8 m |
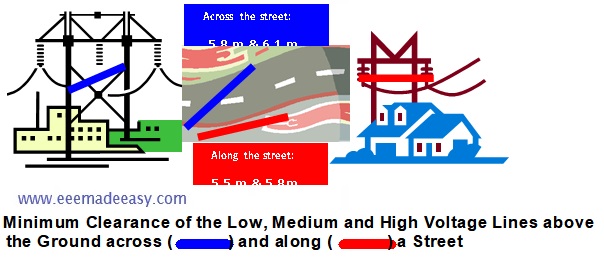
The clearance above ground of overhead line conductor erected elsewhere other than along or across street is given in Table below.
| VOLTAGE LINES | CLEARANCE ABOVE GROUND |
| Low, medium and high voltage lines up to 11kv (Bare) | 4.6 m |
| Low, medium and high voltage lines up to 11kV (insulated) | 4.0 m |
| High voltage lines above 11 kV | 5.2 m |
| Extra high voltage lines | 5.2 m plus 0.3 m for every 33kV |
minimum clearance from buildings of low and medium voltage lines and service lines
As per Rule 79, the minimum clearance from buildings of low and mediumvoltage lines and service lines is shown in Fig below.
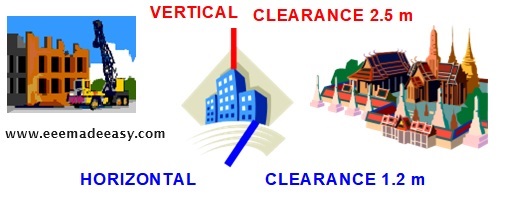
Any conductor less than the above clearance should be adequately insulated and should be attached at suitable intervals to bare earthed bearer wire having a breaking strength of not less than 350 kg.
IE Rule 80
As per Rule 80, the clearance of high and extra high voltage lines from buildings is as under:
Vertical clearance:
a. High voltage including 33kV 3.7 m
b. Extra high voltage 3.7 m + 0.3m for every additional 33kV or part thereof.
Horizontal clearance:
a. High voltage up to 11 kV 1.2 m
b. Voltage above 11 kV 2.0 m
c. Extra high voltage lines 2.0 m + 0.3m for every additional 33 kV or part thereof.
IE Rule 87
Rule 87 gives the minimum clearances between lines when crossing each other (Table below).
| System Voltage | 11 – 66 kV | 110 – 132 kV | 220 kV | 400 kV | 800 kV |
| Low and medium | 2.44 | 3.05 | 4.58 | 5.49 | 7.94 |
| 11 – 66 kV | 2.44 | 3.05 | 4.58 | 5.49 | 7.94 |
| 110 – 132kV | 3.05 | 3.05 | 4.58 | 5.49 | 7.94 |
| 220 kV | 4.58 | 4.58 | 4.58 | 5.49 | 7.94 |
| 400 kV | 5.49 | 5.49 | 5.49 | 5.49 | 7.94 |
| 800 kV | 7.94 | 7.94 | 7.94 | 7.94 | 7.94 |
As per the table the minimum clearance between any two 11 – 66 kV lines should be 2.44 m.
Similarly, the minimum clearance between the 11 – 66 kV lines and 110 – 132 kV lines should be 3.05 m when these cross each other, and so on.
IE Rule 90
Rule 90 is about earthing and states that all metal supports and metallic fittings should be permanently and efficiently earthed.
Each stay-wire should be efficiently earthed or an insulator provided in it at a height not less than 3.0 m from the ground.
IE Rule 94 – 108
Rules 94 to 108 are about electric traction
IE Rule 109 -132
Rules 109 to 132 give the additional precautions to be adopted in mines and oil fields
IE Rule 133 -143
Rules 133 to 143 cover miscellaneous aspects.
IE Rule 138-141
Rule 138 to 141 give the penalties for broken seal and for breach of other rules.
IE Rule 142
Rule 142 is about the application of rules
IE Rule 143
Rule 143 is about Repeal.
Under this rule The Indian Electricity Rules, 1937 have been repealed: Provided that any order made, notification issued or anything done or any action taken under any of the said rules should be deemed to have been made, issued, done or taken under the corresponding provisions of the rules.
Download IE Rules 1956
Read Also
- [Updated]List of IS Codes Electrical standards|IS 732, IS 3043 etc|Indian electrical standards
- [Class A,B,C]Electrical Contractor Licence in Kerala Class A, Class B, Class C|How to get Electrical Contractor License Kerala|Electrical Supervisor Permit A and B
- [Complete Guide] Class A Electrical Contractor Licence Application, Renewal
- [PDF]IE Rules|Indian Electricity Rules 1956
- Which IE rule is applicable to service mains?|Indian Electricity Rule
- [PDF] Electricity Act 2003|Indian Electricity Act 2003 PDF
- Which act is used to regulate the Indian power sector today?
- Indian Electricity Rules MCQ|IE Rules Questions
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus







