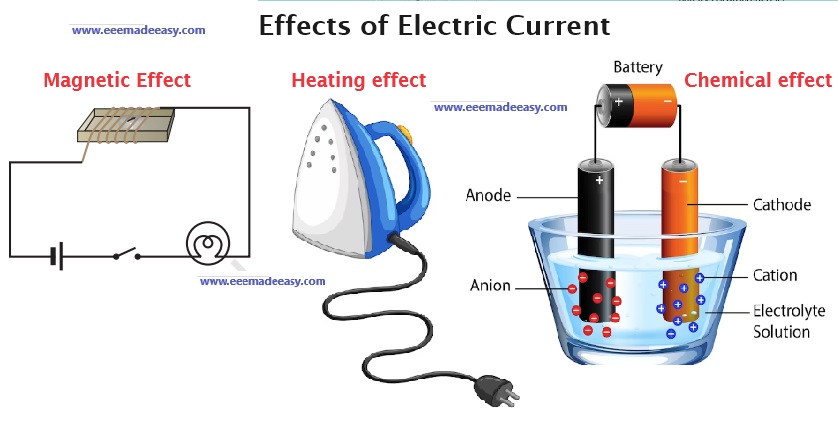
Effects of Electric Current: The three main effects of the electric current are magnetic effect, chemical effect, and heating effect. Let’s discuss some practical applications of the effects of electric current.
Effects of Electric Current
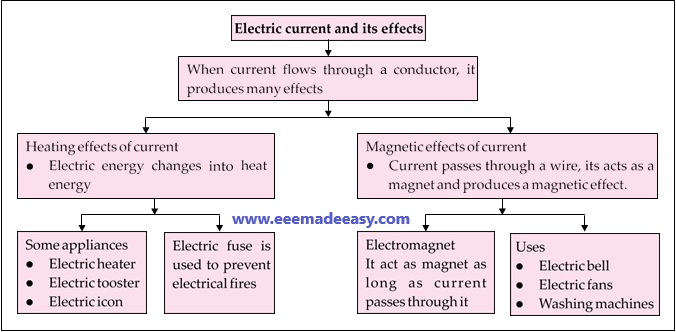
When electrically flows through a conductor, it can produce many effects. We make use of these Effects of Electric Current in various electrical appliances.
When the current flows through a circuit various effects of current happen depending on the components being used.
(a) heating effect of electric current
(b) magnetic effect of electric current
(c) chemical effect of electric current
Some practical applications of the effects of an electric current include:
Magnetic effect: bells, relays, motors, generators, transformers, telephones,
car ignition, and lifting magnets
Chemical effect: primary and secondary cells, and electroplating
Heating effect: cookers, water heaters, electric fires, irons, furnaces, kettles, and
soldering irons.
Heating Effect of Electric Current
The wire or component or device, through which the current passes, becomes hot. This is known as the heating effect of current.
The filament of the bulb is the part which gives light.
When a bulb is connected to a circuit and switched on, its filament becomes so hot that it gives out light.
When a bulb glows for a longer time, the current also flows through it for a longer time, the longer the bulb glows the hotter it becomes.
Therefore it can be concluded that
(i) The current produces a heating effect.
(ii) The heating caused is more if the time for which the current flows is more
It is not only the filament of the bulb, but every wire or component or device, through which the current passes, becomes hot. This is known as the heating effect of current.
Applications of the Heating effect of current
Some appliances such as electric heaters, electric immersion rod, electric toaster, electric iron, etc. also use this property of heating due to electric current.
They have wound coils of wire known as ‘heating element’ through which current flows resulting in its heating due to resistance offered by the wire.
- [Set 1]MCQ’s on Electrical Heating
- [Set 2]MCQ’s on Electrical Heating
- [Set 3]MCQ’s on Electrical Heating
The amount of heat generated in a wire depends on the length and thickness of the wire. Thus for different requirements, the wires of different materials and different lengths and thickness are used.
For example, silver and copper become the least, whereas materials like tungsten and nichrome get too hot on the passage of current through them.
The heating element of a heater becomes red hot but not the connecting wire. Why?
Ans.: This is because the resistance of a heater wire is high, whereas that of the connecting wire is extremely low.
The heat generated in a wire is doubled/halved when both the radius and length of the wire are doubled/halved.
Heating effect of electric currrent
Tungsten and Nichrome Heating elements
Tungsten and nichrome get too hot on passing current through them.
It makes, them useful for making filaments of electric bulbs and other heating devices (Heaters, irons, geysers, toasters etc.)
Electric bulbs have a filament made of tungsten while the filaments of electric iron, electric heaters, geysers, and toasters are made of nichrome.
Tungsten and nichrome have the ability to withstand very high temperature without getting melted.
Electric Fuses
Electric fuse is a safety device used in electrical circuits. It is used to prevent electrical fires and protect electrical devices from damage.
A fuse is a small piece of wire of an alloy (usually 63% tin and 37% lead) Fuse wire should have an adequately low melting point.
There is a maximum limit of the current which can safely flow through a circuit.
If the current exceeds the safe limit, then the fuse wire gets hot and melts.
This creates a gap in the circuit and the appliance is saved from getting burnt.

Always, use proper fuses which have been specified for particular applications, carrying ISI marks. Never use just any wire or strip of metal in place of a fuse.
Miniature circuit breaker (MCB)
miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is also used instead of or in addition to fuses, in household electric circuits.
MCB is a switch that automatically stops the current in a circuit if the current in it exceeds the specified maximum limit.
What are MCBs? How do they work?
Ans. MCBs (Miniature circuit breakers) are switches that automatically turn off when current in a circuit exceeds the safe limit. We turn them on and the circuit is once again complete
What is the difference between a fuse wire and a heating wire?
Ans.: The fuse wire has a low melting point, whereas the heating wire has a high melting point. Fuse wire is made up of tin-lead alloy, whereas heating wire is made of constantan
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
A current-carrying wire behaves as a magnet, as long as current flows through it. This is known as the magnetic effect of current.
When electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet.
Hans Christian Oersted was the first person who noticed the deflection of the compass needle
every time the current was passed through the wire.
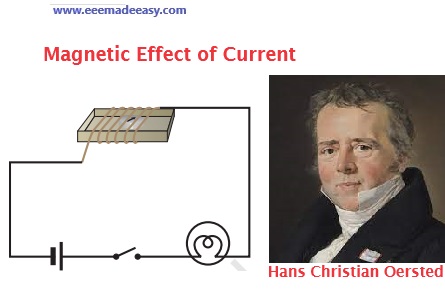
Hans Christian Oersted, one of the leading scientists of the 19th century, played a crucial role in understanding electromagnetism.
In 1820 he accidentally discovered that a compass needle got deflected when an electric current passed through a metallic wire placed nearby.
Through this observation Oersted showed that electricity and magnetism were related phenomena.
His research later created technologies such as radio, television and fiber optics. The unit of magnetic field strength is named the Oersted in his honor.
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is based on the magnetic effect of current. It indicates that it must be a magnet made by using electricity.
An electromagnet consists of a long length of insulated copper wire coiled around an iron rod or a bar.
When the current is passed through this coil, the iron rod behaves like a magnet.
The magnetism of the iron rod disappears as soon as the current through the coil is switched off.
Therefore, an electromagnet is a temporary magnet. Along with the current, the magnetism can also be switched ‘off’ or ‘on’.
The Factors on which the Strength of an Electromagnet depends
The strength of an electromagnet depends directly upon;
- The amount of current flowing through the coil
- The number of turns of copper wire in the coil
- length of the electromagnet
The strength of an electromagnet depends directly upon (i) the amount of current flowing through the coil, and (ii) the number of turns of the coil. It depends inversely upon the length of the coil.
The strength of an electromagnet depends inversely upon the length of the electromagnet, which means the lesser the length of the electromagnet, the more will be the strength of an electromagnet.
- Magnetic field MCQ|Magnetism MCQ Questions & Answers
- Magnetic materials: Dia, Para,Ferro,Ferri and Antiferro magnetic materials
- Magnetism-Methods of Magnetization
Uses of Electromagnets
- in cranes to pick magnetic materials from a junkyard.
- in electric bells
- in loudspeakers
- by doctors to remove iron splinters from eyes
- in electric motors
How does an Electric Bell work?
A U-shaped electromagnet is used in an electric bell. It is magnetized when the push button of the bell is pressed.
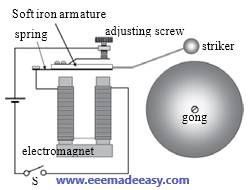
Electric Bell working steps
- Electric Bell consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece.
- The coil acts as an electromagnet.
- An iron strip with a hammer at one end is kept close to the electromagnet.
- There is a contact screw near the iron strip.
- When the iron strip is in contact with the screw, the current flows through the coil which becomes an electromagnet.
- Then it pulls the iron strip.
- In the process, the hammer at the end of the strip strikes the gong of the bell to produce a sound.
- However, when the electromagnet pulls the iron strip, it also breaks the circuit.
- The current through the coil stops flowing.
- The coil is no longer an electromagnet.
- It no longer attracts the iron strip.
- The iron strip comes back to its original position and touches the contact screw again.
- This completes the circuit.
- The current flows in the coil and the hammer strikes the gong again.
- This process is repeated in quick succession.
- The hammer strikes the gong every time the circuit is completed. This is how the bell rings.
Difference between Bar Magnet and electromagnet
| Bar magnet | Electromagnet | ||
| It is permanent magnet. | 1. | It is a temporary magnet. | |
| Its strength cannot be changed. | 2. | Its strength can be changed. | |
| Its uses are limited. | 3. | Its uses are more wide. | |
What are the uses of electromagnets?
Ans.: Electromagnets are used in cars, speakers, electric motors, electric bells, telephone receivers, television, picture tubes etc.
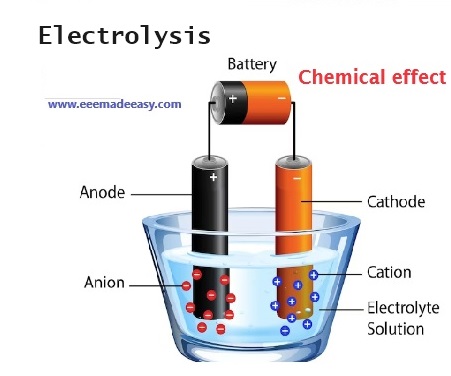
Chemical Effect of Electric Current
The chemical effects of electric current are used in Electrolysis, Electroplating, Electrolytic cells etc
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus