Charging Methods and Power Ratings for Elecric Vehicles are explained in this post. Check the Electrical Vehicle Charging standards also.
Charging Methods & Power Ratings
Read Also: Electric Vehicle Terminologies
Electric Vehicle charging involves supply of direct current (DC) to the battery pack.
As electricity distribution systems supply alternate current (AC) power, a converter is required to provide DC power to the battery.
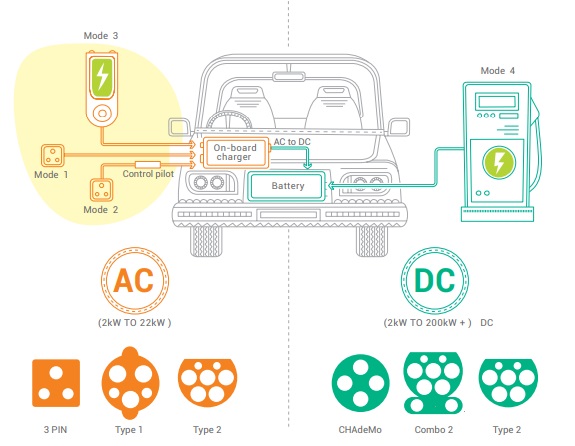
Conductive charging can be AC or DC.
In the case of an AC EVSE, the AC power is delivered to the onboard charger of the EV, which converts it to DC.
A DC EVSE converts the power externally and supplies DC power directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger.
Download & Install Job Search India App for daily Job Updates

AC and DC charging are further classified into four charging modes, with Modes 1-3 pertaining to AC charging and Mode 4 pertaining to DC charging.
Modes 1 and 2 are applicable for connecting an EV to a standard socket outlet, utilizing a cable and plug.
Mode 1, also known as dumb charging, permits no communication between the Electric Vehicle and EVSE and its use is not recommended.
The portable cable used in Mode 2 has an inbuilt protection and control capability and
is typically used for home charging.
Modes 3 and 4, which provide a separate charger device to supply power to the EV, have improved control systems and are used for commercial or public charging
EVSE Power Ratings
Power Ratings of EVSE
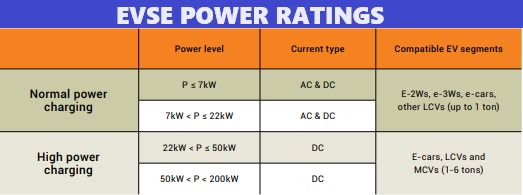
EVSEs have different power ratings or levels based on charging requirements, which in turn determine the input power requirements for charging infrastructure.
Table 2 categorizes EV charging by power level, with normal power charging going up to 22kW and highpower charging going up to 200kW.
While EVSEs with power ratings up to 500kW are globally available, they are largely applicable for heavy vehicles like buses and trucks.
Normal power AC charging is adequate for e-2Ws, e-3Ws and e-cars. Normal power DC charging is unique to India, due to the prevalence of LEVs, and the use of low-voltage batteries in e-cars.
Single-phase AC chargers, with a maximum power rating of 7kW, are adequate for LEVs and cars with single phase on-board chargers.
Three-phase AC chargers, with a power rating up to 22kW, are required for e-cars with larger onboard chargers.
Input power supply for normal power charging can be provided from the standard electricity
distribution network.
For high-voltage e-cars with battery capacities between 30-80kWh, high-power DC charging of 50kW is used.
The power level of DC chargers in the market ranges between 25kW and 60kW.
However higherpowered DC chargers will be available in the near future.
While high-power DC charging takes less time for e-cars, it requires higher electricity supply with additional infrastructure.
Normal power charging points are therefore adequate for most charging requirements, including slow or overnight charging of e-cars.
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
Read more on Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle
- Electric Vehicle Terminologies
- Electric Vehicle Charging Standards
- Charging Methods & Power Ratings for Electric Vehicles
- Electric Vehicle charger|EVSE- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
Join EEE Made Easy Whatsapp Channel
Best Handheld Home Electric Vehicle Chargers
- Zevpoint Portable EV Charger/ Ropeset for Cars
- Portable EV Charger Fast 7.4kW (32A) with LCD Display Current Adjustment and 5 Meter Cable
- Zevpoint Swift Pro Electric Vehicle Charger | 7.2 kW, Type 2 Connector, Single Phase, 20 feet Cable | Touch Screen, Power Control, Smart
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus