QUESTION CODE : 073/2022
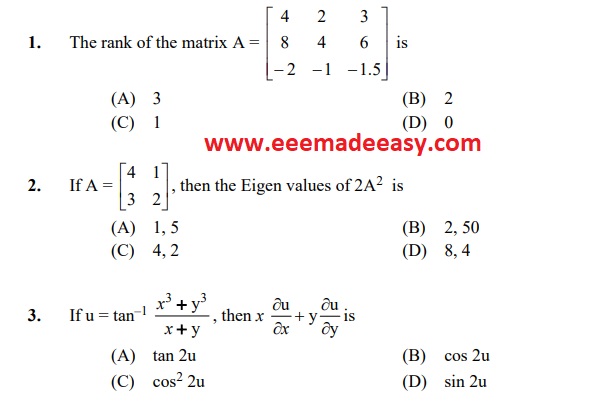
Assistant Engineer Kerala State Pollution Control Board
Cat. No :124/2021
Download & Install EEE Made Easy App
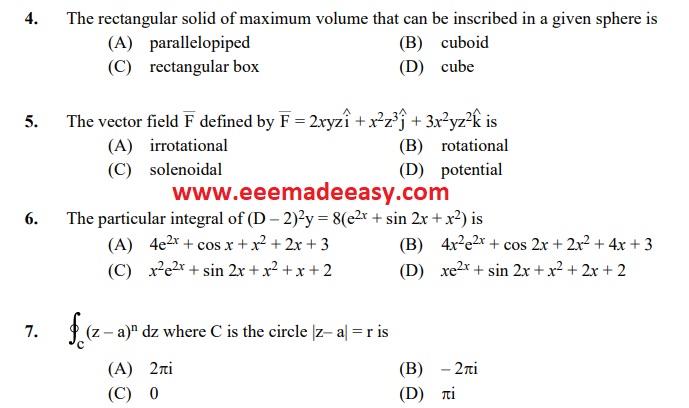
MEDIUM OF QUESTION : English
DATE OF TEST: 28.06.2022
DATE OF UPLOAD : 29.06.2022
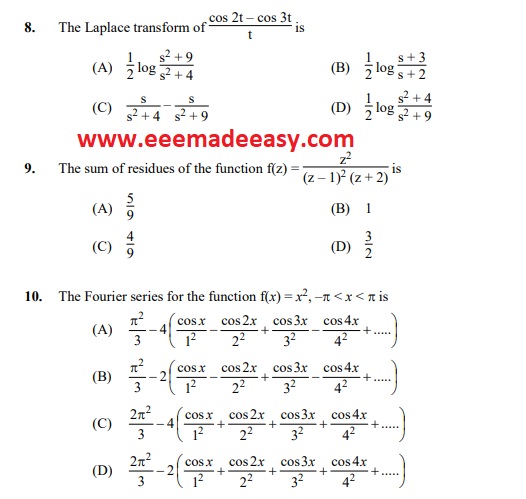
- A simply supported beam I carries a point load at its mid span. Another identical beam II
carries the same load but uniformly distributed over the entire span. The ratio of
maximum deflections for I and II will be
(A) 2/3 (B) 3/2
(C) 8/5 (D) 2/5 - A body is said to be in equilibrium if,
(A) No force acts on it.
(B) Resultant of all the forces acting on it is zero.
(C) Algebraic sum of all the forces in the X direction, Y direction and moment of
all the forces about any point is equal to zero.
(D) All the above
- For the principal axes of a section
(A) Sum of moment of inertia is zero.
(B) Difference of moment of inertia is zero.
(C) Product of inertia is zero.
(D) None of these. - The maximum compressive strain in concrete at the outermost compression fibre in
bending is
(A) 0.002 (B) 0.0035
(C) 0.67 (D) 0.42 - According to IS 456-2000 the modulus of elasticity of concrete is
(A) directly proportional to compressive strength
(B) inversely proportional to compressive strength
(C) directly proportional to square root of compressive strength
(D) inversely proportional to square root of compressive strength - For a simply supported beam of span 8 m, the minimum effective depth to satisfy the
vertical deflection limits should be
(A) 400 mm (B) 310 mm
(C) 450 mm (D) 600 mm - Out of the following, select the most suitable type of bolt that can be used, when the bolts
are subjected to reversal of stresses.
(A) Ordinary unfinished bolt (B) Flange bolt
(C) Turned and fitted bolt (D) High strength bolt - Horizontal stiffener is provided in a plate girder to safe guard against
(A) Shear buckling of web plate (B) Compression buckling of web plate
(C) Yielding (D) All of the above - The main function of alumina in brick earth is
(A) To impart plasticity (B) To make the brick durable
(C) To prevent shrinkage (D) To make the brick impermeable - Le-Chateliers equipment is used for determining the
(A) Setting time of cement (B) Soundness of cement
(C) Tensile strength of cement (D) Compressive strength of cement - A crack is formed in a RCC beam, when the material exceeds
(A) modulus of elasticity (B) compressive stress
(C) modulus of rupture (D) None of the above
- The type of pile recommended in places where the soil is soft and that reduces the risk of
liquefaction
(A) Friction pile (B) Pedestal pile
(C) Pressure pile (D) Vibro pile - Which one of the following represents an event ?
(A) Fixing of door (B) Concrete cured
(C) Selecting sites (D) Plastering of walls - The time by which a particular activity can be delayed without affecting the preceding
and succeeding activities is known as
(A) Total float (B) Interfloating float
(C) Free float (D) Independent float - Pick up the incorrect statement from the following.
(A) No deduction is made for the volume occupied for reinforcement.
(B) No deduction is made for the openings up to 0.1 sq.m.
(C) No deduction is made for the volumes occupied by pipes, not exceeding 100
sq.cm in cross-section.
(D) None of the above. - Consistency of cohesive soils is related to its
(A) Density (B) Moisture content
(C) Shear strength (D) Porosity - Sheep foot rollers are best suited for compacting which type of soil ?
(A) Granular soils (B) Cohesive soils
(C) Hard rock (D) Any type of soil - In Mohr’s circle, a point located above Mohr’s envelope shows
(A) Imaginary condition (B) Safe condition
(C) Imminent failure condition (D) Condition of maximum obliquity - A wall is acted upon by a pressure due to water on one of its sides. If w = Specific weight
of liquid, and H = Height of liquid, total pressure on the wall per unit length is
(A) wH (B) wH/2
(C) wH2
/2 (D) wH2
/3 - The use of a surge tank is
(A) to control the pressure variations due to rapid changes in the pipe line flow.
(B) to eliminate water hammer possibilities.
(C) to regulate flow of water to turbines by providing necessary retarding head of
water
(D) All of the above
- A standard Cipoletti weir is __ in shape.
(A) Rectangular (B) Triangular
(C) Trapezoidal (D) Circular - For highway capacity design, what are the studies needed ?
(A) Origin and destination studies (B) Parking and accident studies
(C) Speed and volume studies (D) Accident studies - In concrete pavements, tie bars are used in which joints ?
(A) Expansion joints (B) Contraction joints
(C) Warping joints (D) Longitudinal joints - Mention the test done to find the extent of weathering of aggregates in a lab.
(A) Soundness test (B) Crushing test
(C) Impact test (D) Abrasion test - The central location of bubble in a levelling instrument means the axis of the bubble tube
is parallel to
(A) Line of sight (B) Line of collimation
(C) Axis of the telescope (D) None of these - Which method is used to locate the position of a station with reference to three known
points ?
(A) Intersection method (B) Radiation method
(C) Resection method (D) Three-point problem - Solution of Three point problems can be obtained by
(A) mechanical method (B) graphical method
(C) trial and error method (D) All of the above - Infiltration capacity depends upon
(A) rainfall intensity
(B) initial moisture condition of soil
(C) soil characteristics and ground slope
(D) All the above. - The rim of a standard rain gauge is _ above ground level.
(A) 10 cm (B) 20 cm
(C) 30 cm (D) 50 cm - The ratio of the volume of water retained by the formation after it has been drained under
gravity to the total volume of formation is known as
(A) yield (B) porosity
(C) specific yield (D) specific retention
- Coliforms which are the indicator organisms for microbiological pollution are
(A) Gram +ve bacilli (B) Gram – ve bacilli
(C) Gram +ve cocci (D) Gram – ve cocci - Kjeldahl Nitrogen is a measure of
(A) Ammonia & Organic Nitrogen (B) Nitrate & Nitrite
(C) Ammonia & Nitrite (D) Nitrate & Organic Nitrogen - 30 ml of sample is pipetted directly to 300 ml incubation bottle. The initial DO of the
diluted sample is 8 mg/L and final DO is 1 mg/L. The initial DO of the dilution water is
9 mg/L and final DO is 8 mg/L. The temperature of incubation is 20°C for 5 days. What
is the 5 day BOD of the sample ?
(A) 180 mg/L (B) 600 mg/L
(C) 61 mg/L (D) 80 mg/L - For slow sand filters the effective size of the sand ranges from
(A) 0.45 mm – 0.55 mm (B) 0.5 mm – 0.6 mm
(C) 0.09 mm – 1.0 mm (D) 0.25 mm – 0.35 mm - Colloids become destabilized when
(A) Repulsive force >Van der Waals force
(B) Van der Waals force > Repulsive force
(C) Gravitational force > Viscous force
(D) Viscous Force > Gravitational force - On analysis for coliform group using 3 samples of 10 mL, 50 mL and 500 mL by
membrane filter technique the results obtained are: 10 mL portion- 5, 6, 7, 8, 9; 50 mL
portion- 30, 35, 26, 36, 38; and 500 mL portion- 300, 380, 340, 360, 320. The number of
coliforms per 100 mL is
(A) 100 (B) 66
(C) 320 (D) 35 - Oxidation of nitrites to nitrates is done by
(A) Nitrobacter (B) Nitrosomonas
(C) Pseudomonas (D) Azetobacter - Form of chlorine, which can prevent the formation of disinfection by products (DBP)
some of which are carcinogens, is
(A) Bleaching powder (B) Chlorine tablets
(C) Gaseous Chlorine (D) Chloramines
- Determination of chemical elements that compose the solid waste is known as
(A) Proximate analysis (B) Energy analysis
(C) Ultimate analysis (D) Inert value analysis
- Type 2 settling is also known as
(A) Discrete settling (B) Compressed settling
(C) Stage settling (D) Flocculent settling - Maximum runoff will be obtained for a rain having duration equal to
(A) Time of concentration (B) Overland flow time
(C) Channel flow time (D) Gutter flow time - A city has a population of 20000 with an area of 1000000 Square metres. The average
runoff coefficient is 0.72 and time of concentration 30 minutes. The maximum storm
water discharge is
(A) 1 Cumec (B) 10 Cumecs
(C) 40 Cumecs (D) 4 Cumecs - Streeter-Phelps equation gives
(A) Total organic content (B) Biochemical oxygen demand
(C) Dissolved oxygen deficit (D) Chemical oxygen demand - Dairy wastes are mainly treated by
(A) Photocatalysis (B) Chemical oxidation
(C) Activated sludge process (D) Phytoremediation - Major component contributing to total solids in Sulfite waste liquor is
(A) Calcium (B) Sulphur
(C) Sugar (D) Lignin - The atmosphere is said to be unstable when
(A) Environmental lapse rate < Adiabatic lapse rate (B) Environmental lapse rate = Adiabatic lapse rate (C) Environmental lapse rate > Adiabatic lapse rate
(D) Environmental lapse rate does not have any relation with Adiabatic lapse rate - “Fanning” the spreading of plume horizontally occurs when the lapse rate is
(A) Negative (B) Positive
(C) Neutral (D) Adiabatic - Which among the following control device has the maximum particulate removal
efficiency ?
(A) Cyclone separator (B) Spray Tower
(C) Fabric Filter (D) Cyclone scrubber
- The process of heating the solid wastes in an oxygen free atmosphere splitting the
organic substances through thermal cracking and condensation is
(A) Incineration (B) Gasification
(C) Spreader Stoking (D) Pyrolysis - According to IS 10500:2012, the acceptable limit of turbidity is
(A) 1 NTU (B) 5 NTU
(C) 10 NTU (D) 2 NTU - The most common disposal method for nuclear waste is:
(A) Microbial uptake (B) Pyrolysis
(C) Incineration (D) Burial in concrete containers - The unit of frequency of sound is:
(A) Decibel (dB) (B) Hertz (Hz)
(C) m/s (D) Lambda - Itai-Itai disease is caused by the heavy metal:
(A) Cadmium (B) Mercury
(C) Chromium (D) Lead - When the rate of deoxygenation is more than the rate of reaeration,
(A) DO increases (B) DO deficit decreases
(C) DO deficit increases (D) Ultimate BOD increases - Which of the following sets out the criteria for an environmental management system and
can be certified to ?
(A) ISO 18001 (B) ISO 14001
(C) ISO 9000 (D) ISO 9001 - The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty that commits state parties to:
(A) reduce greenhouse gas emissions (B) reduce ozone depleting substances
(C) reduce acid rain (D) reduce photochemical smog - The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to:
(A) reduce greenhouse effect (B) protect ozone layer
(C) reduce acid rain (D) reduce photochemical smog - What is the unit for Carbon footprint ?
(A) tonnes of CO2
equivalent (B) hectares of land
(C) mg/litre of air (D) no unit
- According to the environmental clearance process in India, Environmental Impact
Assessment is not needed for projects which fall under:
(A) Category A (B) Category B1
(C) Category B2 (D) Schedule I - Which of the following Acts came into existence in India, to enact the decisions made in
the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment held in Stockholm in June,
1972, in which India participated ?
(A) The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
(B) The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
(C) Forest Conservation Act, 1980
(D) The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 - The process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide is called:
(A) Global warming (B) Carbon foot-printing
(C) Carbon crediting (D) Carbon sequestration - How many Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) have been adopted as 2030 Agenda ?
(A) 5 (B) 15
(C) 17 (D) 20 - Which of the following is a popular Green building rating system, developed in India ?
(A) LEED (B) BREEAM
(C) Green Globes (D) GRIHA - The permissible limit of lead (Pb) in drinking water as per IS 10500:2012 is:
(A) 0.01 mg/l (B) 0.05 mg/l
(C) 0.005 mg/l (D) 0.001 mg/l - Using of plants to clean up contaminated environments is called:
(A) Bioremediation (B) Phytoremediation
(C) Nanofiltration (D) Root zone filtration - Molarity of aqueous solution of acetic acid containing 30 weight percentage acid if
density of solution is 1 g/cc is
(A) 5 (B) 2.5
(C) 2 (D) 0.05 - Wet leather with moisture content 60% enters a drier and leaves with 10% moisture. If
output from the drier is 100 kg/h, amount of water removed in kg/h is
(A) 225 (B) 100
(C) 200 (D) 125
- Relative humidity of air can decrease in spite of increase in humidity if
(A) pressure is increased (B) temperature is increased
(C) temperature is decreased (D) cannot happen - At low concentration of a gas in a liquid, which of the following laws is most
appropriate ?
(A) Raoult’s law (B) Henry’s law
(C) Dalton’s law (D) Amagat’s law - Heat required to raise temperature of 1 kg solution, with mean specific heat capacity
3.5 kJ/kgK), from 300 K to 400 K is______
(A) 700 kJ (B) 700 J
(C) 350 J (D) 350 kJ - Boiling point of a heterogeneous mixture is
(A) same as that of high boiling component
(B) same as that of low boiling component
(C) less than boiling point of all the components
(D) more than boiling point of all the components - Temperature at which equilibrium vapour pressure of a liquid equals existing partial
pressure of vapour in a mixture is the mixture’s
(A) dew point (B) boiling point
(C) freezing point (D) sublimation point - Components A and B react to form product C, as per the reaction, A + B C. Heat of
combustion for A, B and C are respectively 330 kcal, 200 kcal and 500 kcal. Standard
heat of the reaction is
(A) 30 kcal (B) – 30 kcal
(C) – 530 kcal (D) 530 kcal - Adiabatic flame temperature of a fuel, attained by burning the fuel with theoretically
required amount of pure Oxygen is 1215 K. If theoretically required amount of air is used
instead of pure Oxygen, the flame temperature can be
(A) 1215 K (B) more than 1215 K
(C) less than 1215 K (D) cannot be predicted - Pressure drop in a packed bed for high Reynolds number is given by
(A) Kozeny Carman equation (B) Burke Plummer equation
(C) Bernoulli’s equation (D) Hagen Poiseuille equation
- Third law of thermodynamics states that
(A) All spontaneous processes are accompanied by degradation of energy
(B) All spontaneous processes are to some extent irreversible
(C) Energy can neither be created nor destroyed
(D) At absolute zero, entropy of a pure crystalline substance is zero - If two Mixed Flow Reactors in series are used for a second order reaction, which of the
following arrangements will perform better ?
(A) Smaller reactor first, followed by a larger reactor
(B) Larger reactor first, followed by a smaller reactor
(C) Two equal sized reactors in series
(D) All the above give same performance

- Pick out wrong statement.
(A) Maximum possible extent of a reaction is given by thermodynamics.
(B) Factors influencing rate of reaction are obtained from chemical kinetics.
(C) Heat liberated or absorbed during a reaction can be calculated from
thermodynamic data.
(D) For all reactions, thermodynamic information alone is sufficient for design. - Constant volume hydrometer is used to measure
(A) density (B) viscosity
(C) pressure (D) composition
- Pirani gauge is used for the measurement of
(A) atmospheric pressure (B) high vacuum
(C) very high pressure (D) moderate pressure - Which of the following cannot be used for composition analysis ?
(A) hydrometer (B) Mass spectrometer
(C) X-ray diffraction (D) Thermal conductivity cell - If a reaction proceeds with increase in number of moles, presence of inert in the system
will
(A) increase equilibrium yield (B) decrease equilibrium yield
(C) not change equilibrium yield (D) cannot be predicted - Steps involved in a Carnot cycle are
(A) Two isothermals and two isobarics
(B) Two isothermal and two isentropics
(C) Two isobarics and two isochorics
(D) Two isentropics and two isobarics - Which of the following is an extensive property ?
(A) density (B) specific heat capacity
(C) entropy (D) molar entropy - For a system consisting of ‘p’ phases and ‘c’ components, if number of independent
reactions involved are ‘r’, number of degrees of freedom is given by
(A) F = c – p + 2 (B) F = c – p + r + 2
(C) F = c – p – r – 2 (D) F = c – p – r + 2 - Negative value of Joule -Thomson co-efficient indicates
(A) Decrease in temperature of gas on throttling
(B) Increase in temperature of gas on throttling
(C) Temperature of gas remains constant on throttling
(D) Joule -Thomson co-efficient is not related to temperature change - If 14 g of nitrogen and 4 g of hydrogen undergo reaction to produce ammonia, the
product stream contains (assume complete conversion of limiting reactant)
(A) 2 g hydrogen and 17 g ammonia
(B) 7 g nitrogen and 17 g ammonia
(C) 1 g hydrogen and 17 g ammonia
(D) 17 g ammonia alone
Answer Key
Check other Answer Keys
- [Answer Key] Assistant Engineer KSEB 2023 Solved Paper|KSEB AE Answer Key 98/2023
- [Answer Key]Assistant Professor Computer Science and Engineering Technical Education Engineering Colleges
- [Answer Key]KSEB Sub Engineer Exam Answer Key|KSEB Sub Engineer Exam Question Paper 2023 Solved
- [Answer Key] Pump Operator Universities in Kerala Exam Answer Key|019/2023 Question paper with Answer Key|557/2021 Solved Question paper
- [Answer Key]Assistant Engineer Kerala State Pollution Control Board Solved paper
- [Answer Key]Engineering Assistant ( Electronics)/ Overseer Gr I (Electronics) provisional answer Key
- [Answer Key]Engineering Assistant ( Electronics)/ Overseer Gr I (Electronics) provisional answer Key
- KWA Operator Exam Answer Key|Answer key Operator Kerala Water Authority
- [Final Answer Key] Electrical Supervisor Apex Societies Answer Key|Answer Key Kerala PSC Electrical supervisor
- [Final Answer KEY]Lineman PWD Electrical Wing Kerala PSC|Answer Key Lineman 258/2021 category
- Solved Paper Electrician- cum- Mechanic 503/2019 |118/2023 Final Answer Key
- [Final KEY PDF]Assistant professor Electrical and Electronics Engineering Kerala PSC Answer Key|724/2021 answer Key|080/2023 Answer Key
- Industries Extension Officer Syllabus Kerala PSC|IEO 2024 Syllabus
- [PDF]Trade Instructor Gr.II Electroplating Syllabus Kerala PSC|92/2023 syllabus
- [PDF] Syllabus Assistant Engineer Electrical Harbour Engineering Kerala PSC
- Industries Extension Officer Kerala PSC Notification|IEO 2024
- Electricity Act 2003 Section 135
- Synchronous Motor Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
- [Latest]Assistant Director industries and commerce Kerala PSC syllabus|630/2023 syllabus






